SAP ASAP Methodology, which stands for Accelerated SAP, is a framework designed to accelerate the SAP implementation process. It offers a structured approach to implementing SAP solutions, ensuring that projects stay on track and meet their objectives. This article will explore the critical steps involved in executing the SAP ASAP Methodology, allowing organizations to harness the full potential of their ERP system.
SAP ASAP Methodology
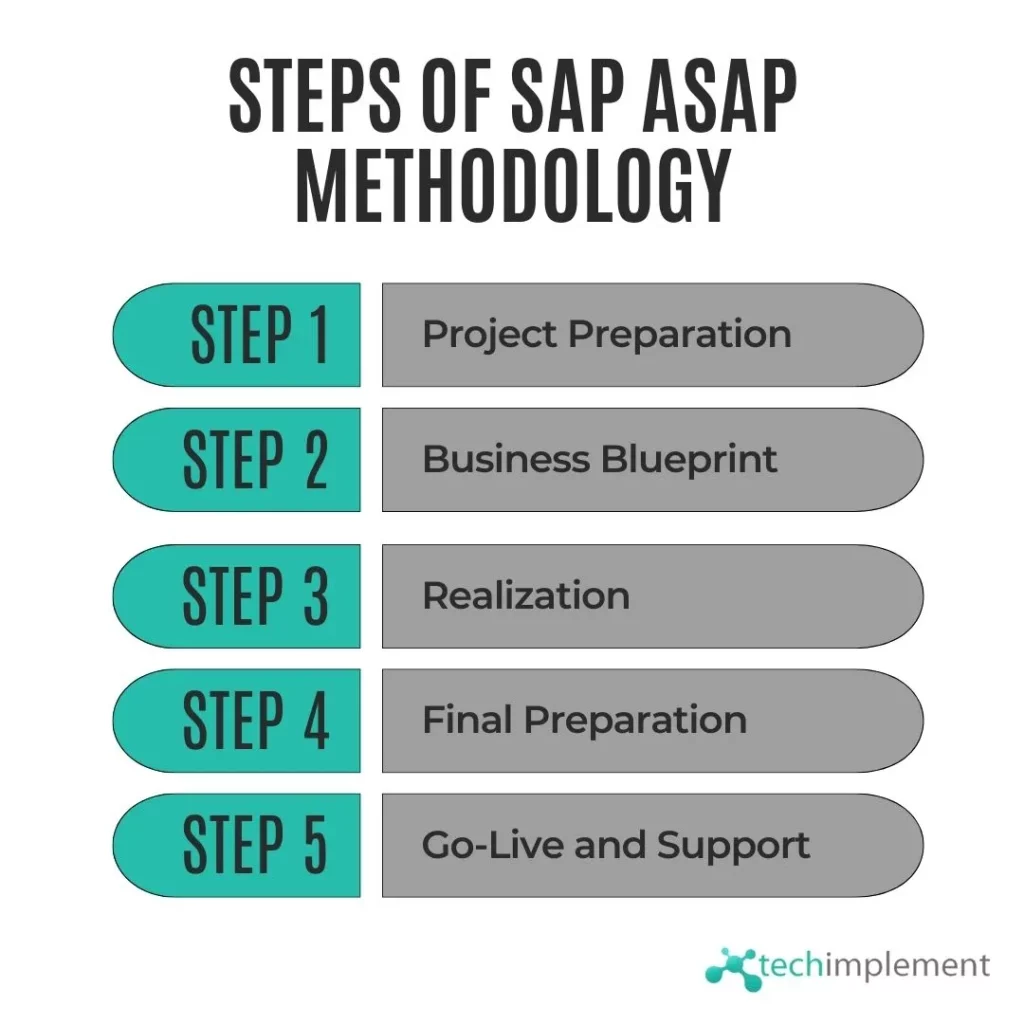
Before going into the details of SAP ASAP Methodology, it’s essential to understand its core principles. This methodology comprises five phases, each with a specific set of tasks and objectives:
Project Preparation: In this initial phase, project objectives are defined, and the project team is assembled. Clear goals and team structure are essential for a successful SAP implementation.
Business Blueprint: This phase involves documenting business processes and customizing SAP to meet the organization’s needs. It’s crucial to align SAP with your business requirements during this phase.
Realization: The Realization phase focuses on building the SAP system and conducting integration testing. Customizations identified in the Business Blueprint are implemented here.
Final Preparation: Data migration and end-user training occur in this phase. Data quality and training are critical components for a smooth Go-Live.
Go-Live and Support: The final phase involves the actual system Go-Live and post-implementation support. It’s a critical step in transitioning to the new SAP system.
Benefits of SAP ASAP Methodology
The benefits of implementing the SAP ASAP Methodology are manifold. This framework:
- Ensures project alignment with business goals.
- Minimizes project risks and uncertainties.
- Facilitates efficient use of resources.
- Speeds up project delivery.
A Guide to SAP ASAP Methodology
Step 1: Project Preparation
Defining Objectives
The first step in the SAP ASAP Methodology is to define clear project objectives. What do you want to achieve with the SAP implementation? Establishing goals will guide the project throughout its lifecycle.
Assembling the Project Team
Assemble a skilled and dedicated project team. Each team member should have a defined role and responsibilities. Effective teamwork is essential for project success.
Step 2: Business Blueprint
Documenting Business Processes
Document all existing business processes. Understanding current workflows helps customize SAP to fit your organization’s needs effectively.
Customization Requirements
Identify customization requirements based on your business processes. SAP should be tailored to meet your specific needs and objectives.
Step 3: Realization
Building the SAP System
During the Realization phase, the SAP system is built according to the customization requirements outlined in the Business Blueprint.
Integration Testing
Thoroughly test the integrated SAP system to ensure that all customizations work seamlessly. Identify and resolve any issues before proceeding.
Step 4: Final Preparation
Data Migration
Migrate data from the old system to the new SAP system. Data accuracy and quality are paramount for a successful transition.
End-User Training
Train end-users to use the new SAP system effectively. User adoption is critical to realizing the benefits of SAP ASAP Methodology.
Step 5: Go Live and Support
System Go-Live
Initiate the SAP system Go-Live. Transition smoothly from the old system to the new one to avoid disruptions in operations.
Post-Implementation Support
Provide support to end-users after Go-Live. Address any issues and ensure the system functions optimally.
Common Challenges and Solutions:
During SAP implementation, several challenges may arise. Two common challenges are related to change management and data quality issues.
1. Change management:
It is the process of helping employees adapt to new systems and processes. It is crucial for a smooth transition. To address this challenge, organizations should invest in comprehensive change management strategies. These strategies include communication plans, training programs, and involving employees in decision-making. This ensures that employees understand and embrace the changes introduced by SAP effectively.
2. Data Quality:
Data quality issues can also hinder the success of SAP implementation. Data quality can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and accurate reporting. To avoid this, organizations should perform data cleansing before data migrating data to the new system. Implementing data governance policies and monitoring data quality can help maintain high data standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SAP ASAP Methodology offers a structured approach to implementing SAP solutions efficiently. By following the outlined steps and addressing common challenges, organizations can successfully plan and execute the SAP ASAP Methodology for a seamless ERP project. If you need any help in executing the SAP ASAP Methodology, then contact us and we will make everything right for you.




