The Complete Guide to Dynamics 365 Field Service (2026)
Contact Us
Field service operations fail when systems don't communicate. Technicians drive back for forgotten parts, dispatchers juggle spreadsheets, customers wait without updates, and managers lack visibility into technician locations or job progress.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Field Service creates a unified digital ecosystem connecting scheduling intelligence, mobile execution, IoT sensors, and AI decision support. This guide examines how D365 addresses core field service challenges and which organizations benefit most from its Microsoft-centric approach.
What is Dynamics 365 Field Service?
Dynamics 365 Field Service is Microsoft's cloud platform for managing field operations built on Dataverse, enabling native integration with Microsoft's business ecosystem while maintaining field service-specific workflow logic.
The platform emphasizes three principles: schedule optimization through constraint-based algorithms, mobile-first execution where technicians control workflows from handheld devices, and ecosystem leverage where Microsoft investments amplify capabilities. It targets organizations operating 20-2,000+ technicians across manufacturing, utilities, healthcare, and telecommunications, where enterprise capabilities justify the investment.
Core Features of D365 Field Service
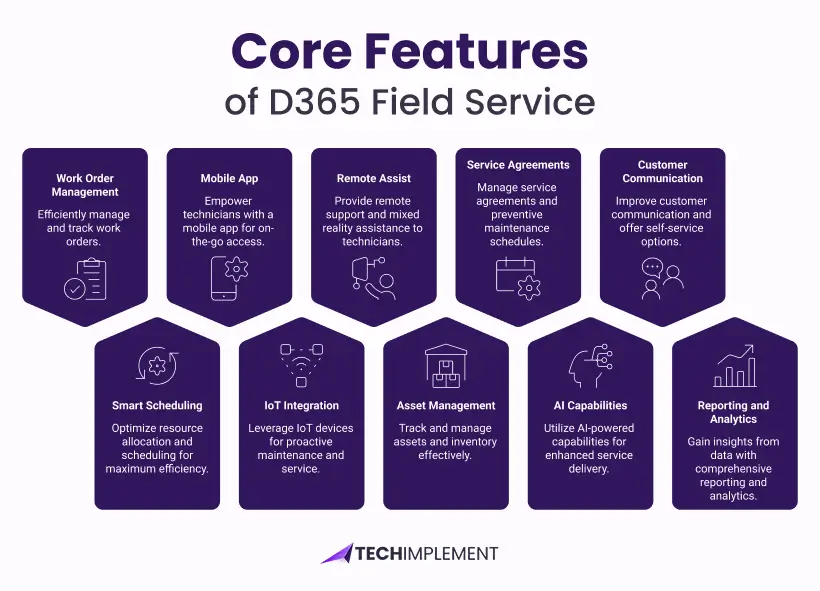
Work Order Management
The work order engine converts customer requests into structured execution plans from multiple triggers: service tickets, IoT sensors, scheduled maintenance, or customer portals. Each order carries metadata defining scope, urgency, skills, parts forecasts, and service history.
The lifecycle engine enforces state transitions from scheduling through completion and invoicing. Checklist templates ensure consistency, while real-time synchronization means desktop dashboards show identical status to field updates, eliminating the lag of batch processing systems.
Smart Scheduling and Resource Optimization
The Schedule Board visualizes technician calendars, locations, skills, and workload across time horizons. Dispatchers drag-and-drop bookings while viewing certifications and drive times with integrated traffic data.
Resource Scheduling Optimization (RSO) uses AI to simultaneously optimize across drive time, working hours, skill matching, parts availability, and customer windows. It operates in single-day, multi-day, or emergency modes with semi-automated dispatcher approval or fully automated execution within defined parameters.
Mobile App for Technicians
The mobile application shifts control to field technicians who possess current job condition information. Daily schedules display with integrated mapping, customer history, and service preferences. Barcode scanning links parts to inventory, digital signatures eliminate paperwork, and photo documentation creates visual proof.
Offline operation handles basement equipment rooms and remote locations lacking connectivity. The mobile database caches work orders, customer data, inventory, and equipment history. Background synchronization exchanges data automatically when connectivity returns without technician intervention.
IoT and Connected Field Service
Connected Field Service shifts economics from reactive repair to proactive intervention. Azure IoT Hub receives equipment sensor data measuring temperature, vibration, pressure, and operating hours. Rule engines evaluate data against threshold models, determining normal versus anomalous behavior.
When equipment deviates from expected patterns, automated work orders spawn with sensor context, historical data, and AI-generated parts predictions. Manufacturing scenarios demonstrate value: vibration sensors detect bearing degradation weeks before failure, enabling scheduled maintenance during planned downtime rather than emergency shutdowns. Organizations achieve 40-60% unplanned downtime reduction and 20-30% lower maintenance costs.
Remote Assist and Mixed Reality
Remote Assist solves expertise distribution where complex repairs require knowledge concentrated in senior technicians. Video calling connects field workers to experts, while mixed reality overlays annotations on physical equipment anchored to specific components.
HoloLens 2 enables hands-free operation with holographic instructions. Integration with work orders provides experts access to service history and documentation during calls. Call recordings preserve training content. Organizations measure 30-40% first-time resolution improvements and decreased expert travel costs.
Asset and Inventory Management
Asset lifecycle tracking creates institutional memory from installation through replacement. Service notes, parts replacements, warranty status, and performance trends accumulate, enabling pattern recognition for recurring failures or premature replacement needs.
Hierarchical modeling represents complex systems like building HVAC with multiple components. Inventory tracks parts across warehouses, vehicles, and trucks. Consumption triggers when technicians mark parts used, with AI analyzing job types to suggest which parts to carry, reducing warehouse trips by 15-20%.
Service Agreements and Preventive Maintenance
Service agreements convert ad-hoc relationships into predictable revenue. Contract terms define frequency, covered equipment, and billing. Automation generates work orders without manual tracking.
Triggers accommodate different maintenance philosophies: calendar-based for regular intervals, meter-based for runtime, or IoT-based for performance degradation. Pricing models support fixed fees, per-incident charges, or hybrid structures. Entitlement tracking flags when usage exceeds terms.
AI-Powered Capabilities (Copilot)
Copilot applies large language models to field service contexts. For technicians, it distills work orders into summaries highlighting priorities, recurring problems, and safety precautions. Parts prediction analyzes relationships between descriptions and historical consumption. Knowledge search surfaces solutions from past resolutions.
For dispatchers, Copilot recommends optimal assignments, drafts customer messages, and forecasts job durations based on historical patterns, improving schedule accuracy.
Customer Communication and Self-Service
Automated communication keeps customers informed without dispatcher intervention: appointment confirmations, day-before reminders, en-route notifications with arrival times, and completion summaries.
The customer portal inverts traditional models. Self-service scheduling displays available slots, photo uploads document issues before arrival, and service history access eliminates record request calls. Post-service surveys capture feedback tied to specific jobs, feeding performance management and retention risk signals.
Reporting and Analytics
Standard reports track work order volume, technician productivity, first-time fix rates, resolution time, parts usage, and customer satisfaction without customization.
Power BI integration enables cross-functional analysis combining field service with financial and sales data. Custom dashboards answer business questions about revenue per technician, equipment quality issues, and certification correlations. Real-time updates support responsive management rather than retrospective analysis.
Pricing Breakdown
D365 Field Service pricing follows Microsoft's user-based licensing model rather than transaction or usage-based structures. Organizations pay per-person per-month based on their role and required access levels.
Main License ($95/user/month)
Provides complete platform access for dispatchers, managers, and technicians. Includes work order management, scheduling, mobile application, reporting, and administrative configuration. This represents the primary license type for active participants.
Team Member License ($8/user/month)
Delivers read-only access for peripheral users requiring visibility without editing rights. Executives reviewing performance dashboards, warehouse staff checking parts availability, or accounting personnel verifying billing data use this lower-cost option.
Device License ($160/device/month)
Covers shared equipment like vehicle-mounted tablets accessed by multiple technicians throughout shifts. Economic analysis determines whether individual user licenses or device licenses cost less based on sharing patterns and total user counts.
Add-On Capabilities
RSO automated scheduling adds $30 monthly per user benefiting from the optimization algorithms. Remote Assist mixed reality collaboration adds $65 monthly per user requiring expert consultation capabilities. Connected IoT integration carries no licensing surcharge though Azure IoT Hub infrastructure incurs separate cloud service costs.
Implementation Investment
Beyond licensing, organizations budget for data migration, transferring customer records and service history from legacy systems ($15,000-$50,000 typical). Configuration and customization adapting the platform to specific business processes runs $25,000-$100,000+ depending on complexity. Training ensures user adoption ($5,000-$20,000). Ongoing partner support provides technical assistance ($3,000-$10,000 monthly).
A representative 50-user implementation totals $150,000-$300,000 first-year all-in cost. ROI models typically show 12-18 month payback through efficiency gains, cost reductions, and revenue growth.
How the Platform Compares to Competitors
Microsoft's Solution vs Salesforce Field Service
Salesforce pricing starts attractively at $50 monthly per user for Service Cloud foundation, but operational capabilities require add-ons pushing total costs to $150-$165 per fully configured user. The Microsoft platform's $95 flat rate proves more economical for organizations needing complete functionality immediately.
Salesforce advantages include faster deployment timelines (4-8 weeks versus 3-6 months for the Microsoft solution) due to more standardized implementation methodology. Organizations already operating on Salesforce CRM gain integration benefits. The AppExchange marketplace offers thousands of pre-built extensions, though quality varies widely.
Microsoft's strengths center on ecosystem leverage. Power Platform enables low-code customization where business users build workflows without developer involvement. Offline mobile capabilities prove more robust where technicians work in connectivity-challenged environments. Azure IoT integration provides enterprise-grade sensor data processing for predictive maintenance scenarios.
Selection Guidance
Choose Salesforce when already standardized on their CRM, requiring the fastest possible deployment, or serving residential markets where Salesforce maintains a stronger partner ecosystem. Choose the Microsoft platform when Microsoft 365 forms your collaboration foundation, offline operation proves critical, or IoT-driven predictive maintenance represents a strategic priority.
Microsoft's Solution vs ServiceNow Field Service Management
ServiceNow pricing begins around $100 monthly per user but enterprise configurations commonly reach $150-$200 once necessary modules combine. ServiceNow's enterprise ITSM heritage creates powerful workflow engines and configuration management databases tracking complex asset relationships across IT and facilities domains.
ServiceNow excels for large enterprises already standardized on its IT service management platform who want mobile workforce capabilities to extend their existing investment. The workflow automation capabilities handle complex approval chains and process governance requirements. Asset relationship modeling supports sophisticated dependencies across interconnected systems.
The Microsoft platform provides more intuitive interfaces requiring less training investment. The mobile experience rates higher in technician satisfaction surveys. Implementation proceeds faster for organizations focused solely on technician management than for those with broader ITSM requirements. Cost structures favor Microsoft when full ITSM capabilities aren't required.
Choose ServiceNow when already operating their ITSM platform, managing complex IT infrastructure requiring tight integration, or needing enterprise-scale workflow governance. Choose Microsoft's solution when prioritizing ease of use, mobile experience quality, and cost efficiency for focused deployments.
Microsoft's Solution vs ServiceTitan
ServiceTitan targets $200-$400+ monthly per user, positioning at premium pricing tiers. The platform optimizes specifically for residential services including HVAC, plumbing, and electrical contractors. Features emphasize call center operations, marketing automation, membership programs, customer financing arrangements, and commission-based compensation structures.
ServiceTitan's residential focus delivers capabilities the Microsoft platform lacks: integrated call booking with marketing attribution, membership revenue management, financing options embedding directly in technician workflows, and commission calculations supporting sales-focused service cultures. The trade-off appears in limited B2B capabilities and constrained enterprise scalability.
Microsoft's solution costs 50-70% less while serving B2B commercial and industrial markets more effectively. Enterprise capabilities including ERP integration, advanced asset management, and IoT predictive maintenance address commercial service needs. Multi-site operations and complex organizational hierarchies align with the platform's enterprise design patterns.
Selection Guidance
Choose ServiceTitan exclusively for residential service businesses where call booking, memberships, and financing drive business models. Choose Microsoft's platform for B2B commercial services, industrial maintenance operations, or enterprises requiring ERP integration at substantially lower total costs.
Microsoft's Solution vs Oracle Field Service
Oracle pricing operates on quote-based models typically ranging $100-$150 monthly per user for comparable capabilities. Oracle's strength lies in routing algorithms processing real-time traffic data and sophisticated capacity planning for very large technician populations (1,000+ workers). Telecommunications and utility industries form Oracle's traditional stronghold.
Oracle advantages include proven scalability at massive deployment sizes and routing sophistication handling complex geographic territories. The platform handles multi-national deployments with strong localization support. Capacity forecasting helps large operations plan hiring and territory expansion.
The Microsoft solution provides more accessible user interfaces reducing training requirements. Offline capabilities handle connectivity-challenged environments more gracefully. Total ownership costs run lower through reduced customization needs. Power Platform integration enables business users to extend functionality without heavy development investment.
Selection Guidance
Choose Oracle when operating very large workforces (1,000+ technicians), requiring sophisticated multi-national localization, or already standardized on Oracle business applications. Choose Microsoft's platform for mid-market to enterprise deployments prioritizing user experience, cost efficiency, and ecosystem alignment.
Key Benefits and Expected Outcomes
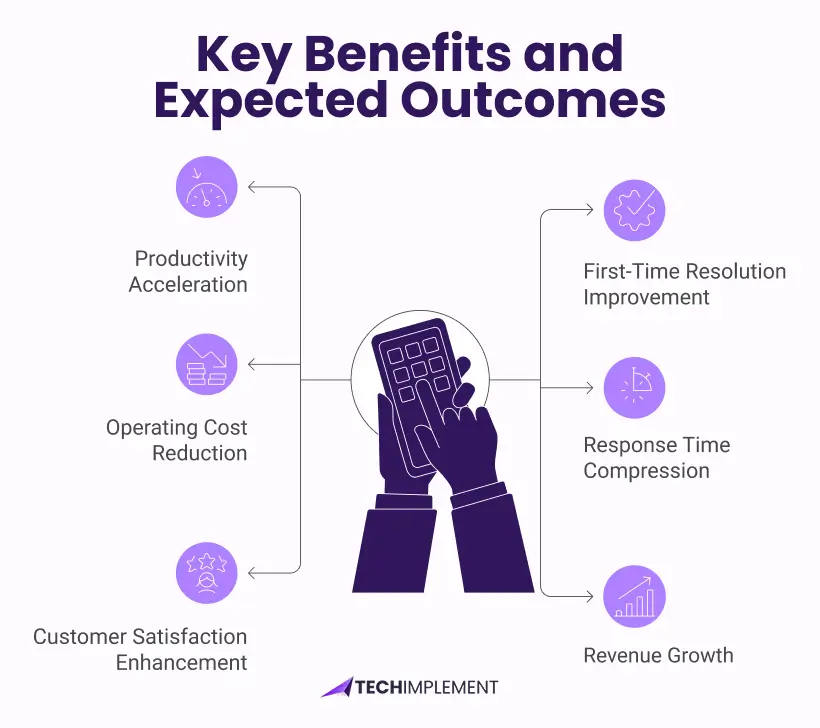
Productivity Acceleration
Optimized routing eliminates wasted drive time between appointments. Technicians complete 15-25% more customer visits daily when the system minimizes unproductive windshield time. Organizations report technicians recapture 45-60 minutes daily previously lost to inefficient routing, parts retrieval, and information gathering.
First-Time Resolution Improvement
AI parts prediction ensures technicians carry required components. Complete equipment history informs diagnosis. Remote expert access solves complex problems without return visits. First-time fix rates rise from industry-typical 50-60% to 70-80%. Each avoided return trip saves $75-$150 in labor and vehicle costs. A 50-technician operation avoiding 500 annual return trips saves $40,000-$75,000.
Operating Cost Reduction
Schedule automation reduces dispatcher headcount requirements by 30-40% while handling larger work volumes. Predictive maintenance prevents expensive emergency repairs. IoT-driven interventions shift 40-60% of work from reactive emergency response to planned maintenance at controlled costs. Inventory optimization releases working capital tied in excessive safety stock by 20-25%.
Response Time Compression
Automated job assignment and optimized routing cut average response times by 25-35%. Organizations with contractual SLA commitments reduce penalty exposures. Emergency calls receive technician dispatch within minutes rather than hours as systems eliminate manual dispatcher workflows.
Customer Satisfaction Enhancement
Proactive communication eliminates information and voids frustrating customers. Accurate arrival estimates and real-time technician tracking increase satisfaction scores 20-30%. Self-service portals shift control to customers who prefer managing their own scheduling. Net Promoter Scores improve as service reliability increases.
Revenue Growth
Higher daily productivity directly expands billable capacity without workforce additions. Improved first-time fix rates eliminate non-billable repeat visits. Service agreement automation captures recurring revenue previously lost to manual tracking failures. Organizations typically measure 8-15% revenue increases within twelve months through pure capacity utilization improvements.
Deployment and Implementation
Implementation Timeline
Platform deployment typically consumes 3-6 months across five phases:
- Planning and Design (4-6 weeks): Requirements workshops, success metrics, scope boundaries, project governance, and change management strategies.
- Data Migration (3-4 weeks): Legacy analysis, extraction, transformation, test migrations, and historical retention policies.
- Configuration and Customization (6-10 weeks): System configuration, custom fields, workflow automation, integration connectors, mobile customization, and report development.
- Testing and Training (4-6 weeks): User acceptance testing, integration testing, performance validation, and role-based training (dispatchers: 2-3 days, technicians: 1-2 days, administrators: 4-5 days).
- Go-Live and Support (2-4 weeks): Cutover execution, hypercare support, performance monitoring, and feedback collection.
Critical Success Factors
Standard features should precede customization by 90+ days following the 80/20 principle: configure extensively, customize sparingly. End-user involvement during design creates ownership and surfaces workflow issues early. Mobile workflows require primary focus since technicians represent the largest user population. Change management separates successful implementations from deployments that users resist. Phased rollouts validate systems with pilot groups before enterprise deployment.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
- Data Quality: Legacy systems contain duplicates and incomplete records. Early profiling identifies remediation needs. Quality rules prevent future degradation.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting to older systems lacking APIs exceeds estimates. Early architecture design and prototypes surface issues before critical impacts.
- Scope Expansion: Formal change control evaluates new requests against original objectives. Non-critical features defer to future phases.
- User Resistance: Focus on personal benefits (easier jobs, better tools) rather than abstract efficiency. Champion networks provide peer support during transitions.
Training and Support Resources
Microsoft Learn offers free self-paced modules with interactive labs organized by role (dispatcher, technician, administrator, developer). Implementation partners bundle training with projects covering actual configurations. Train-the-trainer programs develop internal expertise for ongoing support.
Microsoft Certified: Dynamics 365 Field Service Functional Consultant Associate (exam MB-240) validates configuration expertise. Support tiers include Standard (break-fix), Professional Direct ($1,000/month for faster response), and Premier/Unified (dedicated enterprise resources). Partner support contracts often resolve issues faster through configuration familiarity. Community forums, user groups, and docs.microsoft.com provide additional resources.
Industry-Specific Applications
Manufacturing: Production downtime costs $10,000-$50,000 hourly. IoT sensors on CNC machines and presses stream performance data, revealing degradation. Automated maintenance schedules during planned breaks prevent emergency shutdowns. Results: 60% downtime reduction, 40% lower costs.
Utilities: Service territories spanning hundreds of miles require intelligent dispatching. IoT monitoring of transformers and grid equipment enables proactive interventions. Offline mobile operation ensures remote area productivity. Results: 30% faster emergency response, 25% fewer truck rolls.
Healthcare: Medical equipment demands 99%+ availability. Preventive maintenance ensures certification compliance. Remote expert access resolves complex issues without specialist travel. Results: 99.5% uptime, 60% reduced travel costs, complete audit trails.
HVAC: Managing agreements across hundreds of buildings requires automation. Seasonal demand challenges capacity planning. Customer portals enable tenant self-service. Results: 95% schedule adherence, 40% fewer emergency calls.
Telecommunications: Installation coordination across territories challenges resource management. Mobile checklists enforce quality standards. Network monitoring integration triggers automatic tickets. Results: 20% productivity improvement, consistent quality.
Facility Management: Multi-site portfolios require coordinating various trades. Centralized asset tracking spans entire portfolios. Vendor portals enable subcontractor work order access. Results: 35% faster completion, improved tenant satisfaction.
Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Excessive Customization: Customizing before mastering standard capabilities creates expensive maintenance burdens. Use standard features 90+ days before custom development. Document business justification for each customization. Warning signs: upgrade difficulties, performance issues, escalating support costs.
Insufficient Change Management
Technical deployment without organizational transformation causes adoption failure. Communicate benefits repeatedly, involve end-users in design, establish champion networks. Warning signs: low usage, manual workarounds, complaints about old systems.
Compressed Timelines
Unrealistic schedules omit testing and training. Build 20% schedule buffers, train close to go-live. Warning signs: milestone slippage, quality defects, team stress.
Inadequate Data Preparation
Migration complexity transfers quality problems to new systems. Profile data early, test migrations multiple times, validate thoroughly. Warning signs: missing records, duplicates, broken relationships.
Desktop-Centric Design
Workflows designed for office users fail in mobile contexts. Prioritize mobile experience, test in conditions technicians face, keep forms simple. Warning signs: technicians avoiding mobile apps, incomplete documentation.
Next Steps
- Readiness Assessment: Evaluate technician count, operational bottlenecks, Microsoft product usage, IoT requirements, and implementation budget/timeline.
- Trial Exploration: Microsoft's 30-day free trial enables hands-on testing. Include actual dispatchers and technicians performing representative workflows. Test mobile app in realistic conditions.
- ROI Calculation: Model productivity improvements (15-25% more jobs), first-time resolution gains (50-60% to 70-80%), response time compression (25-35% faster), overtime reduction, and fuel savings.
- Partner Selection: Choose Microsoft partners with operational specialization, industry experience, customer references, certifications, and comparative pricing. Probe implementation methodology, change management, and support models.
- Implementation Planning: Define success metrics, secure executive sponsorship, allocate resources, set realistic 3-6 month timelines, and budget for licenses, implementation, training, plus 20% contingency.
Conclusion: Determining Platform Suitability
The Microsoft solution delivers maximum value for organizations committed to the Microsoft ecosystem or those requiring enterprise capabilities including IoT integration, predictive maintenance, and low-code customization.
Optimal Use Cases: Organizations managing 20-2,000+ technicians needing sophisticated scheduling and mobile capabilities. Microsoft-centric companies using Office 365, Teams, and other modules are gaining seamless integration. Industries prioritizing IoT predictive maintenance, such as manufacturing, utilities, and healthcare require complex third-party integrations to match. Organizations want business-user customization through Power Platform, avoiding development bottlenecks. B2B commercial services require comprehensive asset management, service agreements, and ERP integration.
Alternative Considerations: Operations with fewer than 10 technicians find better value in Jobber or Housecall Pro. Salesforce-invested companies prefer platform consistency. Residential services (HVAC, plumbing, electrical) benefit from ServiceTitan's industry-specific features.
ROI typically occurs within 12-18 months through combined productivity gains, cost reductions, and revenue growth. Success requires realistic planning, strong change management, and disciplined focus on standard features before customization.
FAQs
Standard deployments consume 3-6 months from kickoff through production launch. Simpler implementations with minimal customization and clean data may complete within 8-12 weeks. Complex deployments involving extensive integrations, significant customization, or challenging data migrations may extend to 6-9 months.
The mobile app provides comprehensive offline operation. Technicians access work orders, update status, capture signatures, record time, and document parts consumption without connectivity. Automatic background synchronization handles data exchange when connectivity becomes available without requiring manual intervention or technician awareness.
The solution operates as cloud software requiring only internet connectivity and current web browsers (Chrome, Edge, Safari, Firefox). Mobile applications support iOS 12+ and Android 8+ operating systems. No on-premises server infrastructure or complex network configuration is required.
Power Platform provides extensive customization without traditional coding. Power Apps creates custom forms and mobile applications. Power Automate builds workflow automation. Power BI develops custom analytics dashboards. Organizations must balance customization benefits against maintenance complexity and upgrade complications.
Migration from Salesforce, ServiceMax, ClickSoftware, or legacy systems represents common implementation scenarios. Data migration encompasses customers, equipment assets, service histories, inventory records, and service contracts. Migration complexity and cost depend on data volumes, quality conditions, and structural differences between source and target systems.
No technical user minimum exists, but economic analysis suggests the platform proves most cost-effective with 20+ users. Smaller organizations often find better value-to-cost ratios in platforms purpose-built for small business operations like Jobber or Housecall Pro.
Dispatcher proficiency typically requires 2-3 training days covering scheduling mechanics and work order management. Technician mobile app competency develops through 1-2 training days emphasizing workflows. Administrator capabilities demand 4-5 days addressing configuration, user management, and ongoing maintenance. Most users achieve baseline productivity within their first week.
Complete data export remains available before subscription termination. Microsoft provides 90-day grace periods after cancellation for data retrieval operations. Standard export formats include Excel spreadsheets, CSV files, and direct database access through APIs enabling migration to alternative platforms.


